Sometimes it is helpful to change the People Also Search For area of a Google search. While People Also Search For is algorithmic, and doesn’t respond strongly to SEO tactics, it can often be changed by creating stronger associations between entities. One way to do that is by associating entities, like people, in Wikidata.
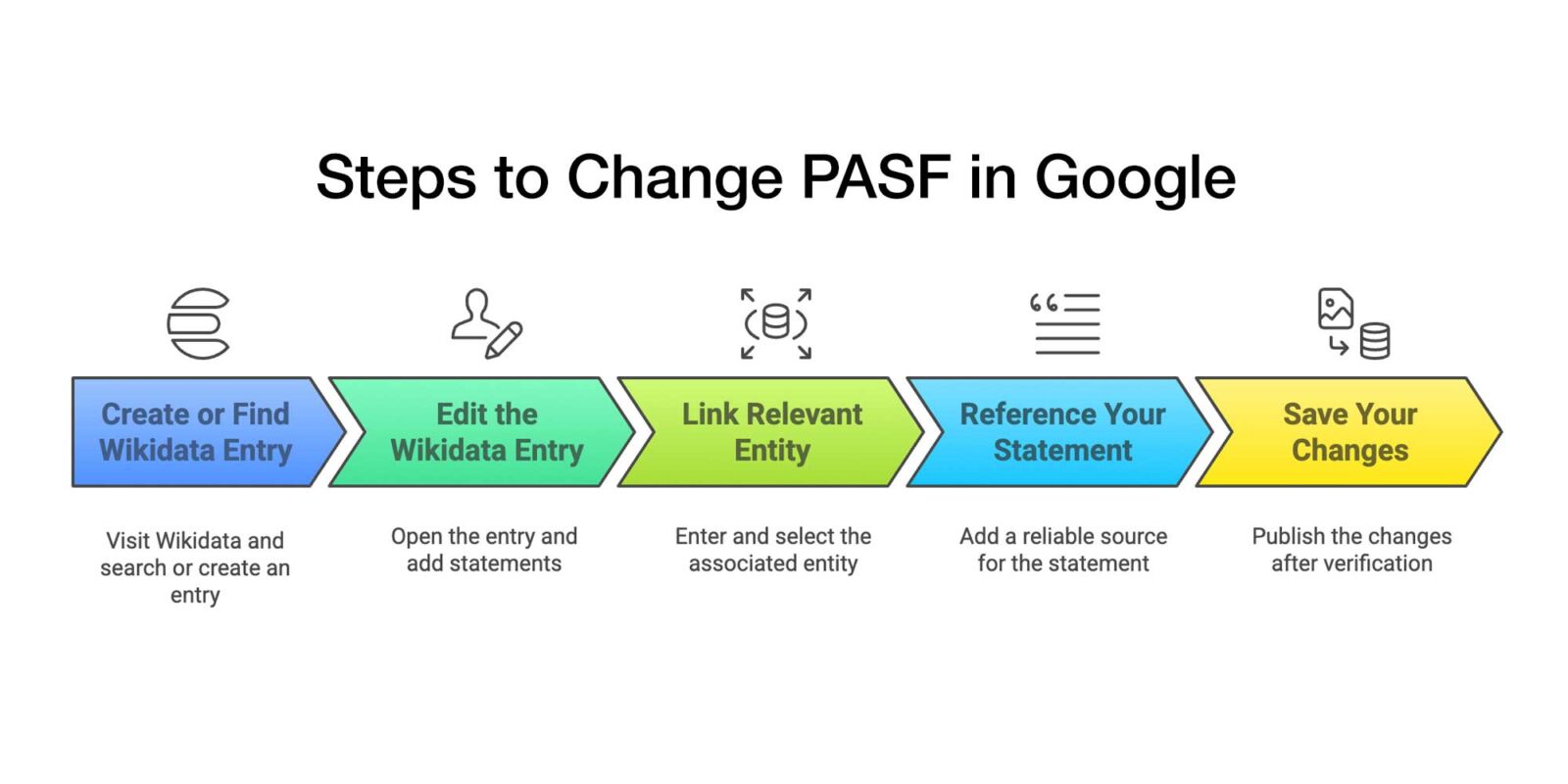
Step 1: Create or Find the Wikidata Entry
- Go to Wikidata: Visit Wikidata.
- Search for the Entity: Use the search bar to find the person or organization you want to edit.
- If the Entity Doesn’t Exist: You’ll need to create a new Wikidata entry by clicking “Create a new Item” and filling in basic details (Label, Description, and Aliases).
Step 2: Edit the Wikidata Entry
- Open the Entry: Once on the item’s page, click “Edit” next to “Statements.”
- Click “Add Statement”.
- Search for the Property to Add:
- For colleagues: Use “colleague” (P3373).
- For mentors: Use “student of” (P1066) or “doctoral advisor” (P184).
- For collaborators: Use “collaborates with” (P1416).
- For organizations: Use “member of” (P463).
Step 3: Link the Relevant Entity
- In the statement field, enter the name of the associated person or organization.
- Select the correct Wikidata entry from the dropdown list.
- (Optional) Add Qualifiers:
- Start Time (P580) and End Time (P582) if the association was during a specific period.
- Position held (P39) if the person held a role in the organization.
Step 4: Reference Your Statement
- Click “Add Reference”.
- Use a reliable source, such as a news article, academic paper, or book.
- Common Reference Properties:
- “Stated in” (P248) for books, articles, or websites.
- “Publication date” (P577) if the source has a specific date.
- “Retrieved from” (P854) for online sources (add the URL).
Step 5: Save Your Changes
- Click “Publish” after verifying your data.
- Check for errors and make sure the associations are accurate.
Associate Owned Web Properties Using Schema
If you own websites that are important and relevant to the entity, you can help Google changes its PASF by changing the schema on the site.
Implement structured data (JSON-LD) on the person’s official website to reinforce entity connections.
{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “John Doe”,
“sameAs”: [
“https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q12345”,
“https://www.wikipedia.org/wiki/John_Doe”,
“https://twitter.com/JohnDoe”,
“https://linkedin.com/in/JohnDoe”
],
“knowsAbout”: [
“https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q67890”
],
“colleague”: [
{
“@type”: “Person”,
“name”: “Jane Smith”,
“url”: “https://www.wikidata.org/wiki/Q98765”
}
]
}
This reinforces entity associations between individuals.
Create & Reinforce PASF Search Patterns
Conduct “Search & Click” Manipulation
- Encourage users to search for a specific term, click your site, and return to SERPs, training Google to associate those terms with your brand.
- Ways to do this:
- Run PPC ads targeting PASF keywords. Some say this is possible, though we do not believe so because organic search and ads are separate systems.
- Email campaigns instructing users to search specific terms. This may work if you have a large email house list.
- Social media challenges encouraging organic searches.
- How It Works:
- Step 1: Announce the Challenge
- Post on LinkedIn, Twitter (X), Instagram, and Facebook: Challenge Alert! Win a free [incentive]
Can you find us on Google? 🔎
Search for: [Target Keyword] + [Your Brand]
Click on our website & find the hidden phrase: “Protect Your Digital Image”
Screenshot it & tag us with the hashtag #NameOfTheChallenge
First 50 participants win [small reward], and 5 lucky winners get and awesome [grand prize]!
- Post on LinkedIn, Twitter (X), Instagram, and Facebook: Challenge Alert! Win a free [incentive]
- Step 2: Drive Searches & Clicks
- Users search for the specific phrase, training Google to associate the keyword with your brand.
- They must click on your site (reducing bounce rates, increasing CTR).
- They take a screenshot of the hidden phrase (forcing engagement).
- Step 3: Encourage Social Sharing